Nibedita Pani
Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University, India
Title: Divalent iron oxidative process for degradation of carbon and nitrogen based pollutants from dye intermediate industrial wastewater
Biography
Biography: Nibedita Pani
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: Water pollution resulting from discharge of partial/not treated textile wastewater containing high carbon and nitrogen pollutants pose a huge threat to environment, ecosystem and human health. It is essential to remove carbon and nitrogen based organic pollutants more effectively from industrial wastewater before discharging. In recent years the removal of nitrogen in particular ammoniacal-nitrogen, nitrate-nitrogen from wastewater is a topic of concern. Wastewater arising from textile operations is characterized to have intense color, high suspended solids, very high concentration of ammoniacal nitrogen and chemical oxygen demand. Ammoniacal nitrogen has adverse effect on aquatic life as well as human being. It acts as one of the main contributor of eutrophication, causes depletion in DO level. The task of treating high to very high concentration of ammoniacal nitrogen is difficult.
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to treat high strength ammoniacal nitrogen and COD (chemical oxygen demand) by Fenton Oxidation process with less detention time from dye intermediate manufacturing industrial wastewater.
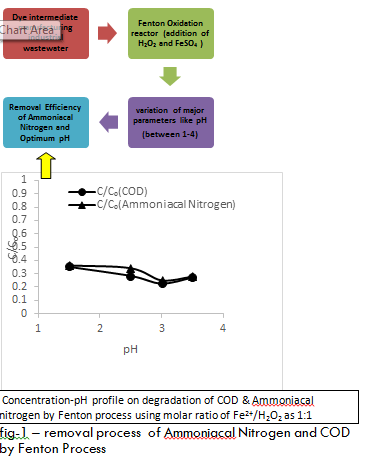
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: Present study focuses on removal of Carbon based pollutant in particular COD and nitrogen based pollutants in particular ammoniacal nitrogen by Fenton Oxidation process using Fe2+ and H2O2 as reagents. The study was carried out with high strength wastewater containing initial COD above 5000 mg/L and NH4+-N above 1000 mg/L. The major operating condition like pH was varied and the effective operating condition was derived.
Findings: The maximum degradation was obtained at pH - 3.0. At this pH the removal efficiencies of COD and ammoniacal nitrogen were found to be 77.27% and 74.9% respectively.
Conclusions & Significance: The Fenton process can be the best alternative for the simultaneous removal of COD and NH4+-N from industrial wastewater.
Figure 1: Concentration-pH profile on degradation of COD & Ammoniacal nitrogen by Fenton process using molar ratio of Fe2+/H2O2 as 1:1- removal process of ammoniacal nitrogen and COD by Fenton Process.